

Ayurvedic Perspective of Arthritis
 Feb 23, 2024
Feb 23, 2024Introduction:
Arthritis is a general term used to describe a group of more than 100 inflammatory joint disorders that cause pain, swelling, stiffness, and decreased joint mobility. The term “arthritis” is derived from the Greek words “arthron,” meaning joint, and “it is” meaning inflammation. While arthritis is commonly associated with older adults, it can affect people of all ages, including children.

Cause of Arthritis
Osteoarthritis
- Natural Aging Process: Osteoarthritis is primarily associated with the natural aging process. Over the years, the wear and tear on joints can lead to the breakdown of cartilage, the protective cushioning between bones in a joint.
- Joint Overuse: Activities and occupations that involve repetitive joint movements or excessive use can contribute to the development of osteoarthritis.
Gout
Hyperuricemia: Gout is caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints. Hyperuricemia, or elevated levels of uric acid in the blood, can lead to the formation of these crystals, causing inflammation and pain in the joints.
Dietary Factors: Certain dietary choices, such as consuming a diet rich in purines found in certain foods and beverages, can contribute to elevated uric acid levels and increase the risk of gout.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Autoimmune Response: Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks the synovium, the lining of the membranes that surround the joints. This immune response leads to chronic inflammation, joint damage, and pain.
Genetic Factors: Genetic predisposition can play a role in the development of rheumatoid arthritis, and certain genetic markers may increase susceptibility.
Understanding the specific causes of each type of arthritis is crucial for accurate diagnosis, effective management, and targeted treatment strategies.

Early Symptoms of Arthritis
- The early symptoms of arthritis can vary depending on the specific type of arthritis a person may be experiencing. However, some common early signs and symptoms that may indicate the presence of arthritis include:
- Joint Pain: Persistent discomfort or pain in one or more joints is a primary early symptom of arthritis. The pain may be dull, aching, or sharp and can range from mild to severe.
- Joint Stiffness: Individuals with arthritis may experience stiffness in the affected joints, especially in the morning or after periods of inactivity. This stiffness can make it challenging to move the joints freely.
- Joint Swelling: Inflammation of the joints is a characteristic feature of arthritis. Swelling may be noticeable around the affected joints, contributing to a feeling of increased size or warmth.
It’s important to note that these early symptoms can be subtle and may come and go, making it challenging for individuals to recognize them. If someone suspects they may be experiencing symptoms of arthritis,

Effect of Arthritis on Our Body
The effects of arthritis on the body can extend beyond the joints, impacting various aspects of an individual’s overall health and well-being. The severity and specific manifestations of these effects can vary depending on the type and progression of arthritis. Here are some common effects of arthritis on the body
- Stiffness and Reduced Mobility: Arthritis often results in joint stiffness, particularly after periods of inactivity or upon waking up in the morning. This stiffness can limit the range of motion in affected joints, making it challenging to move freely.
- Muscle Weakness: Reduced use of affected joints due to pain and stiffness can lead to muscle weakness. Over time, this weakness may affect surrounding muscles, contributing to a decline in overall muscle strength.
- Joint Deformities: In some types of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis, prolonged inflammation can lead to joint deformities. The joints may become misshapen, affecting both appearance and function.
- Bone Erosion: Inflammatory arthritis, particularly rheumatoid arthritis, can result in the erosion of bone and cartilage within the joints. This can lead to joint deformities and a loss of joint function.
It’s crucial for individuals with arthritis to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses both the specific symptoms and the broader impact on their overall health and well-being.
Types of Arthritis:
Understanding the various types of arthritis is crucial for accurate diagnosis and tailored management strategies. Here, we explore some of the most common types:
- Osteoarthritis (OA):
- Description: Osteoarthritis, often referred to as degenerative joint disease, is the most prevalent form of arthritis. It results from the gradual breakdown of joint cartilage, the tissue that cushions the ends of bones.
- Causes: Natural aging, joint overuse, and joint injuries contribute to the development of OA. Over time, the wear and tear on joints lead to pain, stiffness, and reduced flexibility.
- Commonly Affected Joints: Knees, hips, hands, and spine.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA):
- Description: Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks the synovium, the lining of the membranes surrounding the joints. This results in chronic inflammation, joint damage, and pain.
- Causes: The exact cause of RA is unknown, but genetic factors and environmental triggers may play a role. Smoking has been identified as a potential environmental risk factor.
- Commonly Affected Joints: Wrists, knees, and fingers.
- Gout:
- Description: Gout is characterized by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints, leading to inflammation and intense pain. It often affects one joint at a time and is known for sudden, severe attacks.
- Causes: Elevated levels of uric acid in the blood (hyperuricemia) can result from dietary choices, genetic factors, or impaired excretion of uric acid by the kidneys.
- Commonly Affected Joints: Big toe, ankles, knees.
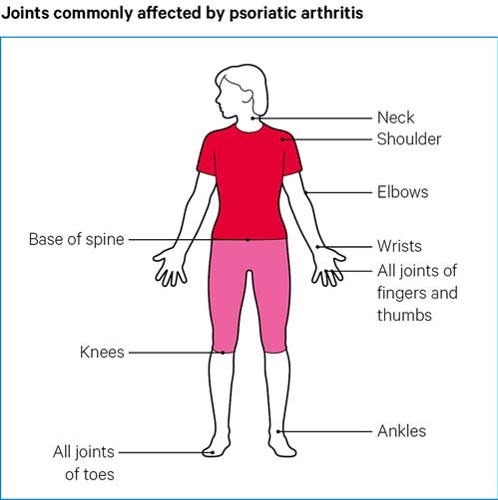
- Psoriatic Arthritis:
- Description: Psoriatic arthritis is a type of inflammatory arthritis that occurs in individuals with psoriasis, a chronic skin condition. It affects both the skin and joints, leading to joint pain, swelling, and skin lesions.
- Causes: The exact cause is unknown, but a combination of genetic, immune system, and environmental factors may contribute.
In conclusion, the diverse nature of arthritis demands a nuanced understanding of each type for effective diagnosis and management.

Ayurvedic Perspective of Arthritis:
Ayurveda, the ancient Indian system of medicine, offers a holistic approach to arthritis. Rooted in balancing the body’s energies, Ayurvedic practices encompass herbal remedies, dietary adjustments, and lifestyle changes. Exploring this perspective provides an alternative avenue for those seeking natural, holistic solutions.
- Dosha Imbalance:
- Ayurveda recognizes three doshas – Vata, Pitta, and Kapha – representing different combinations of the five elements (earth, water, fire, air, and ether) in the body. Imbalances in these doshas are believed to contribute to various health conditions, including arthritis.
- In arthritis, an aggravated Vata dosha is often implicated, leading to dryness, stiffness, and pain in the joints.
- Agni (Digestive Fire) Imbalance:
- Ayurveda emphasizes the role of agni, or digestive fire, in maintaining overall health. Impaired digestion, leading to the accumulation of toxins (ama), is considered a contributing factor to arthritis.
- A compromised digestive system can result in the formation of ama, which circulates in the body and deposits in the joints, triggering inflammation.
Home Remedies for Arthritis:
Home remedies for arthritis focus on natural, accessible methods to alleviate symptoms and improve the overall well-being of individuals dealing with this condition. It’s important to note that while these remedies can be supportive, they should complement rather than replace medical advice and prescribed treatments. Here are some home remedies that individuals with arthritis may find beneficial:
- Turmeric and Ginger Tea:
- Benefits: Both turmeric and ginger have anti-inflammatory properties. Turmeric contains curcumin, which has been studied for its potential to reduce arthritis symptoms.
- How to Use: Make a tea by boiling fresh ginger and adding a teaspoon of turmeric powder. You can also include honey for added taste and potential anti-inflammatory benefits.
- Warm Compress:
- Benefits: Applying a warm compress to affected joints can help reduce stiffness and alleviate pain.
- How to Use: Place a warm towel or a heating pad on the affected joint for 15-20 minutes. Ensure that the temperature is comfortable and not too hot to avoid burns.
- Regular Exercise:
- Benefits: Gentle, low-impact exercises can improve joint flexibility and reduce stiffness.
- Recommended Activities: Swimming, walking, and tai chi are low-impact exercises that can be beneficial for individuals with arthritis.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight:
- Benefits: Excess weight can contribute to increased stress on joints, worsening arthritis symptoms.
- How to Achieve: Adopting a well-balanced, nutritious diet and engaging in regular physical activity can help maintain a healthy weight.

THERAPY OF ARHRITIS
It’s essential for individuals to consult with a qualified Ayurvedic practitioner who can assess their specific dosha constitution and design a personalized treatment plan.
- Panchakarma:
- Description: Panchakarma is a comprehensive detoxification and rejuvenation therapy in Ayurveda. It involves a series of cleansing procedures to eliminate toxins (ama) from the body and balance the doshas.
- Benefits: Panchakarma may include therapies such as Virechana (purgation) and Basti (enema), which are tailored based on the individual’s dosha constitution and the type of arthritis.
- Abhyanga (Ayurvedic Massage):
- Description: Abhyanga involves a full-body massage using warm medicated oils. It is designed to reduce inflammation, improve circulation, and nourish the joints and tissues.
- Benefits: Regular abhyanga is believed to enhance joint flexibility, reduce stiffness, and promote overall relaxation.
- Swedana (Herbal Steam Therapy):
- Description: Swedana involves exposing the body to herbal steam, which helps open up the channels, improve circulation, and relieve stiffness.
- Benefits: This therapy can be particularly beneficial for individuals with arthritis by promoting joint mobility and reducing pain.

Conclusion:
In the intricate tapestry of arthritis, understanding its causes, recognizing early symptoms, exploring diverse types, considering alternative perspectives, and embracing a combination of home remedies and therapeutic approaches are essential. Arthritis is a journey, and armed with knowledge and a comprehensive approach, individuals can navigate it with resilience, aiming not just to manage but to thrive despite its challenges.

